Difference between revisions of "Power System"
(Added picture and description of DC-DC converters.) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* Red: 36V or 48V power | * Red: 36V or 48V power | ||
| − | Main power goes to the E-Bike controller, which converts DC power to three phase AC to drive the electric motor. The circuit board inside the box with the DC-DC converters does some conditioning on the main power before sending it on to the E-Bike controller. | + | Main power goes to the E-Bike controller, which converts DC power to three phase AC to drive the electric motor. The circuit board inside the box (shown in the picture below) with the DC-DC converters does some conditioning on the main power before sending it on to the E-Bike controller. The signal conditioning board has been called the PowerOn board. It initially had three functions: |
| + | 1. Provide a power-on circuit that the Kelly e-bike controllers need. It has a large resistor between the 36V input line and 36V output line. When the switch is thrown, a relay bypasses the resistor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Signal conditioning on phase signals from electric motor to give a fine resolution of vehicle speed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. An Arduino Micro applied the correct PWM signal to the brakes when E-stop was triggered. The Arduino is no longer used, since PWM is no longer used to control brakes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The PowerOn board presently in use implements only the first function. The board is cut and jumpered so that the DPST switch also turns the 12V and 24V lines on/off. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DC-DC converters.JPG|1000px]] | ||
NEXT > [[Low Level]] | NEXT > [[Low Level]] | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 1 July 2019
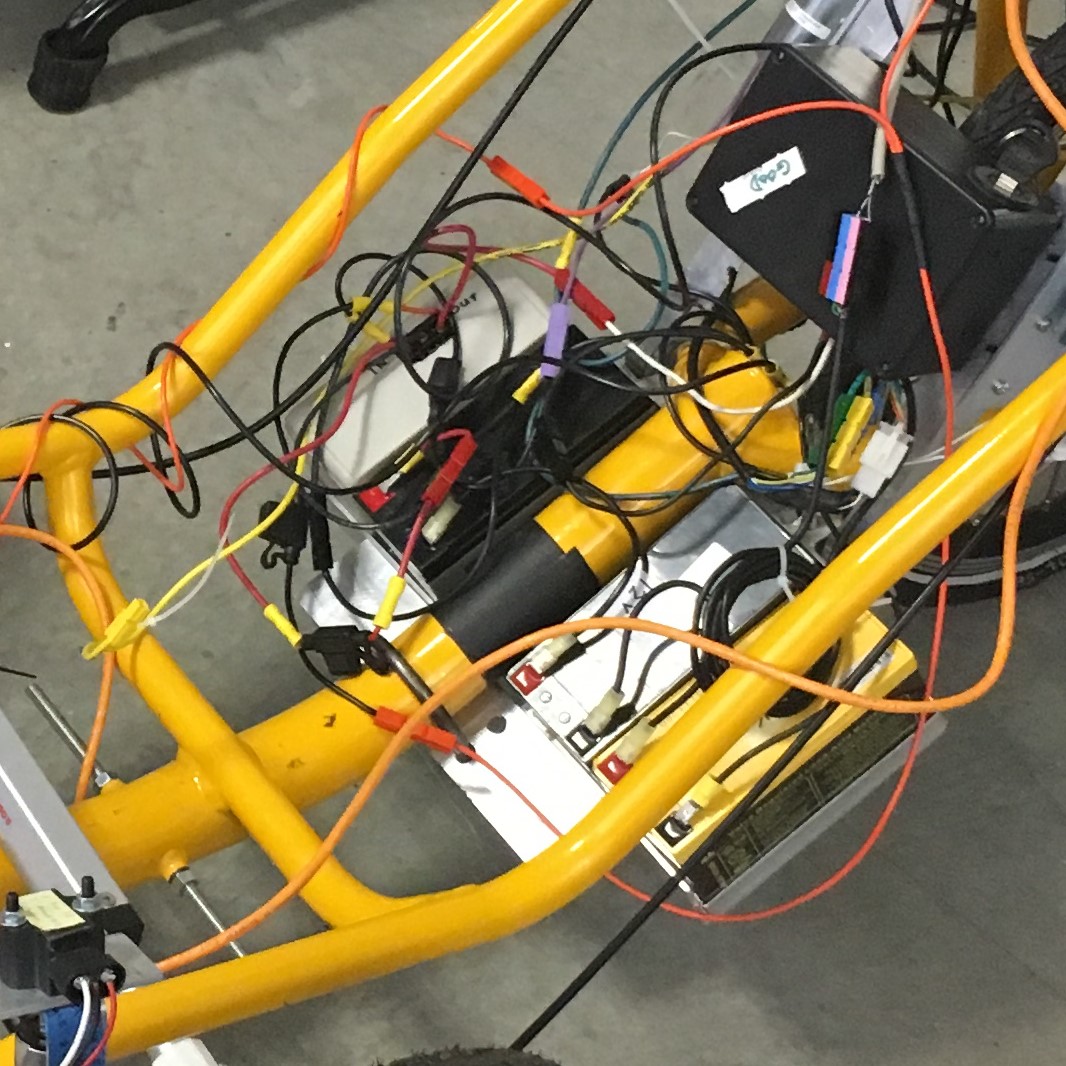
The Elcano power supply is a 36V battery on the Catrike recumbents or a 48V supply on the ELF. The picture shows three 12V lead-acid batteries connected in series to provide 36V. The fourth box in the top of the picture is a plastic case that houses a circuit board and two DC-DC converters. The converters output a 12V supply and a 24V supply. All power lines are color-coded with the right color wire when possible and with the right color Anderson connectors. The power lines are:
- Ground: Black
- Pink: 5V (not commonly used between modules)
- Orange: 12V
The steering servo runs on 12V.
Brakes are held on with 12V.
All Arduinos have a Vin pin that can take 12V. The Arduino internally converts the voltage to 5V and 3.3V.
The four-wire CAN connection consists of CAN hi, CAN lo, Ground, and 12V. This connection powers the Raspberry Pi, Receiver board and Scanse Sweep board.
- Purple: 24V
Used to apply the brakes.
- Green: Either 12V or 24V
This is the power line to the brake solenoids. It is initially 24V to apply the brake, then reduced to 12V to hold the brake on.
- Red: 36V or 48V power
Main power goes to the E-Bike controller, which converts DC power to three phase AC to drive the electric motor. The circuit board inside the box (shown in the picture below) with the DC-DC converters does some conditioning on the main power before sending it on to the E-Bike controller. The signal conditioning board has been called the PowerOn board. It initially had three functions:
1. Provide a power-on circuit that the Kelly e-bike controllers need. It has a large resistor between the 36V input line and 36V output line. When the switch is thrown, a relay bypasses the resistor.
2. Signal conditioning on phase signals from electric motor to give a fine resolution of vehicle speed.
3. An Arduino Micro applied the correct PWM signal to the brakes when E-stop was triggered. The Arduino is no longer used, since PWM is no longer used to control brakes.
The PowerOn board presently in use implements only the first function. The board is cut and jumpered so that the DPST switch also turns the 12V and 24V lines on/off.
NEXT > Low Level